CO2 Storage Consulting
Geologic CO2 Storage Consulting
CCS / CCUS Consulting
Carbon Capture & Storage (CCS) Consulting
Carbon Capture, Utilization & Storage (CCUS) Consulting
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)/ Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS)/ Geological Sequestration of CO2 is emerging as an important tool to get to net-zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 2050 for combating global warming, and over the last few years, has developed rapidly. Although much of the technology is similar to that of CO2 enhanced oil recovery (EOR), as practiced in the Permian Basin of West Texas, and in some other parts of the United States, and in Canada, there are important differences which require adaptation of the industry’s subsurface knowledge to this new application.
The high-level and seasoned consultants of the A&A Consulting Team who have been working on CO2 projects, around the world, since the 1970s, have been providing state-of-the-art consulting services on CCS/CCUS, CO2 EOR, and other related projects, around the world, for many years. But 2021 generated unprecedented momentum behind CCS/CCUS projects, not only in the US, but around the world, and the A&A Consulting Team of high-level and seasoned consultants is delighted to be helping some of the major energy companies on their challenging CCUS/CCUS projects.
As interest in CCS/CCUS/ CO2 geosequestration grows around the world, our experienced CO2 EOR and geomechanics consultants are some of the most qualified and experienced professionals available in the industry to help our clients in their CCS/CCUS/ CO2 geosequestration projects. The high-level and seasoned consultants of the A&A Consulting Team have worked on major CO2 projects since 1970s.
In addition to providing state-of-the art consulting, the seasoned consultants of the A&A Consulting Team conduct a customized one-week training workshop on the topic of 'Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS) / Geological Sequestration of CO2', at our clients' offices, around the world, whenever requested. The seasoned consultants of the A&A Consulting Team, along with other CO2 EOR industry veterans, also volunteer their time and effort to teach a one-day training course on the topic of 'CCUS / Geological Sequestration of CO2' (which is an abridged version of the one-week training workshop that we conduct for A&A clients) in conjunction with the Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE) conferences, around the world. We have taught this one-day training course, in conjunction with several SPE conferences, in North and South America, Europe, and the Middle East, since 2014. The last presentation of this popular one-day training course, was virtual, on May 10, 2021, in conjunction with the SPE Workshop: CCUS in Canada - Opportunities for a Net Zero Future. To read an outline of this popular one-day public training course, please click here.
The high-level and seasoned consultants of the A&A Consulting Team, and collaborators, can help your company to:
1) Characterize the geologic and geophysical features of the identified storage formations
This task will include, but will not be limited, to addressing the following issues:
- Geologic and geophysical characterization
- Reservoir characterization
- Seal characterization
- Structural characterization
- Formation mineralogy
- Fault characterization
- Hydrodynamics
- USDW characterization
- Other important factors
2) Select a site based on geological suitability, long-term well integrity risk, and repository economic viability
This task will include, but will not be limited, to addressing the following issues:
- Site selection
- Injectivity
- Formation parting pressure
- CO2 plume
- Reservoir pressure
- Rock properties
- SCAL data
- Multiple spatial and time scales
- Heterogeneity
- Simulator(s) selection
- Modeling Studies: Geoscientific/static modeling, reservoir/dynamic modeling, and all other types of modeling studies that will be required, for the CCUS project
- Other important factors
3) Transport CO2 from its source(s) to the storage location(s)
This task will include, but will not be limited, to addressing the following issues:
- Evaluation and design of all CO2 processing steps from the source, including capture/separation as needed, dehydration, purification (e.g., O2 removal) and compression to prepare the CO2 for transport.
- Design of the CO2 pipeline (flow analysis, phase behavior, etc.), booster stations, and surface facilities to the injection wellhead.
- Other important factors
4) Obtain and comply with necessary permitting requirements, including but not limited to successful acquisition of Class VI UIC permit(s) and compliance with all other applicable federal, state, and local laws and regulations (including but not limited to relevant rules of the GLO, the Texas Railroad Commission, the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality, the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration, and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency regarding Class VI wells, and carbon dioxide handling, transport, storage, and monitoring)
This task will include, but will not be limited, to addressing the following issues:
- Permitting activities by evaluating routing of pipelines, assessing the CO2 conditions from the source to the injection wellhead (flow, composition, temperature, pressure, phase), and
- Providing other relevant process information required for permit applications.
- Other important factors
5. Construct and operate the contemplated CO2 sequestration facility
This task will include, but will not be limited, to addressing the following issues:
- Start-up, commissioning, and operation of CO2 injection/sequestration projects (with a focus on the process/surface facility operations).
-
Preparation and oversight of equipment fabrication/construction/
installation, development of standard operating procedures, operator training, safety review/HAZOPs, etc.
- Other important factors
6. Identify environmental concerns and develop a plan to address those concerns
This task will include, but will not be limited, to addressing the following issues:
- Identification and mitigation of any environmental issues associated with the processing and transport of CO2 from the source to injection wellhead.
- Other important factors
Planning CCUS Projects Offshore
A technical paper on the topic of ‘Planning EOR projects in Offshore Oil Fields’, presented by Dr. Paul Bondor, Dr. Roger Hite, and Dr. Sam Avasthi, at the SPE Latin American and Caribbean Petroleum Engineering Conference, in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, during June 2005 ( Paper Number: SPE-94637-MS ), is very relevant today, when the oil & gas industry is moving towards planning CCUS projects offshore.
The high-level and seasoned consultants of the A&A Consulting Team are available for brain-storming sessions with your company's professionals and managers to develop detailed project description and scope-of-work (SOW) to meet your company's objectives, and thereafter provide state-of-the-art consulting services to your company on all aspects of its CCS/CCUS projects offshore, including, but not limited to:
(1) Offshore Pipelines Evaluation: To determine which pipelines could be used to transport CO2 offshore, and the required upfront inspection and testing of those pipelines
(2) Offshore Platforms Evaluation: To determine which of the available offshore platforms have the facilities, and which will be available for locating the additional facilities that will be required, for the CCUS project
(3) CO2 Emissions / Emitters Evaluation: Screening of the available sources of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions [onshore powerplants and other industrial plants, and natural gas processing plants (onshore and/or offshore)], for capturing CO2 for the CCUS project
(4) Oil & Gas Reservoirs Evaluation: Screening of oil & gas reservoirs that will be ideal for CO2 enhanced oil recovery (EOR) / enhanced gas recovery (EGR), and/or for CO2 storage, projects offshore
(5) Saline Formation Evaluation: Screening of saline formations that will be ideal for CO2 storage offshore
(6) Modeling Studies: Geoscientific/static modeling, reservoir/dynamic modeling, and all other types of modeling studies that will be required, for the CCS/CCUS project
(7) Economic Studies and Risk Analysis of the planned CCS/CCUS Project Offshore
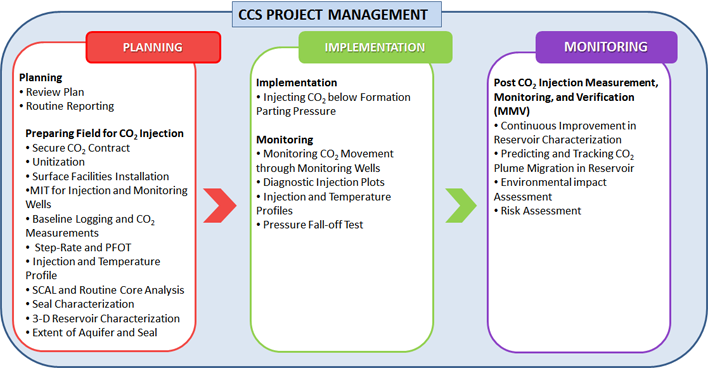
CCS/CCUS Project Development and Management
While all the elements of CCS/CCUS exist, they have yet to be developed to scale or successfully integrated making it an uncharted territory. The structure and future of the CCS/CCUS industry will be shaped by those who have the vision and will to do so, and who possess the knowledge and experience to integrate technology, regulatory structure, and financial incentives into viable projects.
Whenever requested by our clients, A&A consultants work closely with them by taking care of all technical issues of their planned CCS/CCUS projects, while they concentrate on field operational issues, as well as help our clients in dealing with power plant operators, to procure the CO2 supplies, and with the governmental agencies, to secure the necessary funding and approvals.
Issues Facing Large-Scale CCUS Implementation
| Key Issues | CO2 Capture | Transportation | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 Generation |
|
Reliable, cost-effective pipleline system |
|
| Financial Underwriters |
|
Clarify ownership rights and responsibility of:
|
|
| Risk Management | Limits on liability (health, environmental, property, financial) risks provided under national, state, or international law | Leakage risk profiles | Leakage risk profiles |
| Regulations |
Enable international carbon trading and ensures the value of emissions allowances Competition, climate regime commitments, tax policy, financial responsibility, property rights and international treaties |
Greenhouse gas (GHG) accounting procedures, and minimum standard for international CCS site Operating procedures (site selection, injection, and monitoring) will be necessary Liability of CCS, (distinguish between risks assumed by the operator, and those mitigated through regulation, and those that can be transferred) |
|
| Insurance | Cover pollution event liability, business interruption, control of well, transmission liability and geomechanical liability | Cover specified closure and post closure activites |
Key Technologies
As we look to bring CCUS into full operation in the near future, expertise and in-depth experience in following two key technologies will play a critical role:
- Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR): At this time, CO2 injection to increase oil production is the primary economic driver for successful CCS, helping offset costs of capture technology
- Geomechanics: Careful site selection is the single most important way to manage short-term and long-term risks of CCUS (each CCUS project site will be unique requiring methodologies and technologies tailored to the particular circumstances and risks)
The high-level and seasoned consultants of A&A Consulting Team have worked on major CO2 projects since 1970s. With our extensive hands-on project experience in CO2 EOR and geomechanics, we are uniquely qualified to plan, design, evaluate and optimize CCUS/ CO2 geosequestration projects.
CCUS Project Finance and Risk
Investors in wide-scale CCUS implementation want realistic, technically sound and unbiased evaluation of financial opportunity and risk. Simply put, investors want to be certain they are investing in the right people:
- Does the management team have a long and successful track record in planning and implementing projects in highly complex and regulated national/ international environments?
- Are they proven leaders in emerging technologies?
- Do they have the right EOR and geomechanics expertise?
- Have they planned adequately for long-term monitoring, measurement and verification (MMV)?
- Do they execute efficiently and on-time?
- Have they identified and planned for technical, environmental, commercial and operational risks/ uncertainties?
- Does the proposed budget represent true cost?
Legal Development and Expert Testimony
The expansion of CCUS will involve a number of legal and regulatory issues associated with protecting public health, safety and the environment, while ensuring permanent CO2 storage. Lawsuits are inevitable, as is the battle of experts who will be called upon to help determine if the technological assumptions underpinning contracts, licensing agreements and regulations are valid or flawed.
A number of regulatory and legal issues currently impede CCUS development, including, but not limited to:
- Access rights to geological sites
- Surface and sub-surface property rights
- Multiple party injection issues
- Hydrocarbon and mineral rights
- Legacy liability
Managing Risk and Long-term Liability
Long-term security of CO2 storage can only be assured through in-depth geomechanical analysis of all aspects of the site, including its history. A comprehensive strategy for monitoring, measurement and verification (MMV) is required at all phases of a CCUS project to ensure safe transportation, injection and long-term storage of CO2.
Determining the appropriate monitoring techniques in each phase is a key factor for successful geologic storage of CO2, and can provide information to address safety and environmental concerns, and provide verification for national accounting of GHG emissions.
MMV capability will assure the regulators, and other government authorities, who must approve large CCUS projects, by providing confidence in the volumes of CO2 stored to ensure safety, environmental, and commercial viability.
Regulatory Framework
CCUS technology requires an effective framework that includes legal and regulatory templates and guidelines, particularly related to the long-term storage of injected CO2 and must include clear financial incentives for project activities to help overcome the hesitancy of major industry players to expand investment in new CCUS projects. These include, but are not limited to:
- Defining and classifying CO2
- Access and property rights
- Intellectual property rights (IPR)
- Monitoring and verification requirements
- International legislations to prevent contradictory and overlapping rulings
Property Rights and Liabilities
Access to and property rights for the area in which a CCS/CCUS project is undertaken must be defined to encourage investment and properly regulate the storage site.
Property rights determine who has or will have access to a project site and are therefore a crucial aspect of any CCS/CCUS project. The three main areas of property rights include:
- Surface (injection of the CO2)
- Sub-surface (storage of the CO2)
- CO2
Because the definition of property rights also influences liability, each must be clearly defined. It is also critical to determine if, when, and how private liability is transferred to the public sector, establish who determines to whom property rights are granted, public and private methods of acquiring the rights, and how to manage the title of the actual CO2.
A&A Consulting Team of high-level and seasoned CO2 EOR and geomechanics consultants is available to help all stake holders in all aspects of their CCS/CCUS projects.
To put the high-level and seasoned consultants, subject matter experts (SME) in CO2 EOR and geomechanics, of the A&A Consulting Team to work on your company's CCS/CCUS projects, please contact us.







